Architecture is a field that encompasses the design and construction of buildings and other physical structures. The four main types of architecture are classical, Gothic, Renaissance, and modern. Each type has its own unique characteristics and styles, which are influenced by the time period and cultural context in which they were created. Understanding these different types of architecture can provide insight into the history and evolution of building design, as well as the social and cultural values of the time. This article will explore each of the four main types of architecture in more detail, highlighting their key features and defining characteristics. Whether you are an architecture enthusiast or simply curious about the history of building design, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of the four main types of architecture and their enduring legacy.
Brief Overview of Architecture
The Importance of Architecture in Society
Architecture plays a vital role in society as it reflects the cultural, social, and economic values of a community. It shapes the way people live, work, and interact with their environment. The following are some of the reasons why architecture is important in society:
- Reflecting Culture and Identity: Architecture serves as a reflection of a community’s culture and identity. It showcases the values, beliefs, and traditions of a society and helps to preserve its heritage. For example, Gothic architecture in Europe represents the religious and cultural values of the medieval period.
- Enhancing Quality of Life: Architecture plays a significant role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals. It provides comfortable and functional spaces for people to live, work, and socialize. Well-designed buildings can improve the health and well-being of occupants by providing natural light, ventilation, and access to green spaces.
- Promoting Sustainability: Architecture can also promote sustainability by incorporating energy-efficient designs, using eco-friendly materials, and reducing waste. Green buildings, for instance, are designed to minimize their impact on the environment by reducing energy consumption and promoting water conservation.
- Economic Impact: Architecture also has an economic impact on society. It creates job opportunities for architects, engineers, construction workers, and other professionals. Moreover, well-designed buildings can attract businesses and tourists, which can boost the local economy.
- Influencing Social Behavior: Architecture can also influence social behavior by creating spaces that encourage interaction and collaboration. For example, public squares and parks can bring people together and foster a sense of community.
In conclusion, architecture is a powerful tool that can shape society in many ways. It reflects cultural values, enhances the quality of life, promotes sustainability, has an economic impact, and influences social behavior. Therefore, it is essential to understand the importance of architecture in society and to ensure that it is designed and built to meet the needs of current and future generations.
The Evolution of Architectural Styles
Throughout history, architecture has undergone a remarkable evolution, with various styles emerging and developing over time. Each architectural style is characterized by distinctive features, materials, and techniques that reflect the cultural, social, and technological context in which they were created. Understanding the evolution of architectural styles is crucial for appreciating the rich history and diversity of human habitation.
Some of the earliest known examples of architecture are found in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and China. These early structures were typically made of mud bricks, stone, and wood, and were designed to provide shelter from the elements and to protect against external threats. As societies grew more complex, so too did their architectural styles, with monumental temples, palaces, and tombs becoming more common.
During the Classical period, architectural styles became more refined and sophisticated, with the Greeks and Romans developing iconic structures such as the Parthenon and the Colosseum. These structures were characterized by their use of symmetrical proportions, columns, and arches, and were often decorated with intricate sculptures and reliefs.
As the Middle Ages dawned, Gothic architecture emerged in Europe, characterized by its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses. These structures were designed to convey a sense of grandeur and awe, with large cathedrals such as Notre-Dame in Paris becoming some of the most impressive architectural feats of the era.
Renaissance architecture, which emerged in Italy during the 14th century, marked a return to classical ideals, with architects drawing inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman structures. This style was characterized by its use of harmonious proportions, columns, and domes, and was often decorated with ornate sculptures and frescoes.
During the 19th and 20th centuries, a variety of new architectural styles emerged, including Art Nouveau, De Stijl, and Brutalism. These styles were often characterized by their use of new materials, such as steel and concrete, and by their bold, abstract forms and geometric patterns.
Today, architects continue to draw inspiration from a wide range of styles and traditions, constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of form, function, and materials. As our built environment continues to evolve, so too will the architectural styles that shape it.
The Four Main Types of Architecture
When discussing the four main types of architecture, it is important to understand that each type is characterized by a specific set of design principles and styles. These types of architecture include:
- Vernacular Architecture: This type of architecture is often associated with traditional building practices and local materials. It is characterized by its simplicity and functionality, with an emphasis on practicality and durability. Examples of vernacular architecture include farmhouses, log cabins, and cottages.
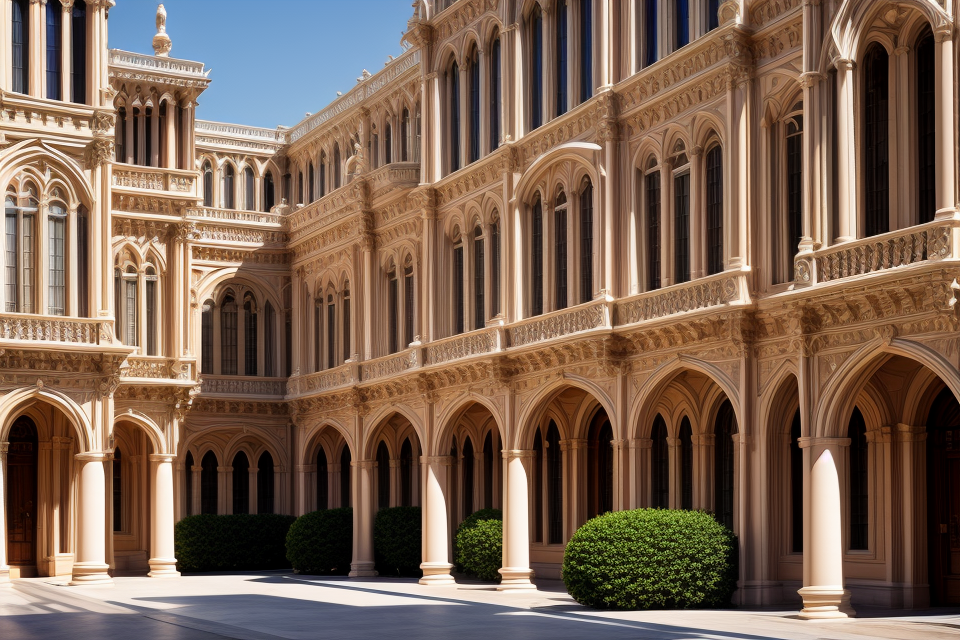
- Classical Architecture: This type of architecture is known for its formal and symmetrical design. It is characterized by its use of columns, pediments, and other classical elements. Examples of classical architecture include the Parthenon, the Colosseum, and the US Capitol Building.
- Gothic Architecture: This type of architecture is known for its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and spires. It is characterized by its intricate and ornate design, with an emphasis on light and space. Examples of Gothic architecture include Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, Chartres Cathedral in France, and Canterbury Cathedral in England.
- Modern Architecture: This type of architecture is known for its minimalist and functional design. It is characterized by its use of clean lines, simple shapes, and new materials. Examples of modern architecture include the Guggenheim Museum in New York, the Seagram Building in New York, and the Sydney Opera House in Australia.
Understanding these four main types of architecture can help you appreciate the diversity and richness of the built environment around us. Whether you are interested in designing your own building or simply appreciate the beauty of architecture, having a solid understanding of these four types is essential.
Classical Architecture
History and Characteristics of Classical Architecture
Classical architecture refers to the style of building design that originated in ancient Greece and Rome, and later evolved during the Renaissance period. This architectural style is characterized by its balance, harmony, and symmetry, which is achieved through the use of a set of guidelines and principles known as the “Classical Orders.”
The Classical Orders are a set of rules that govern the proportion and placement of columns, pediments, and other decorative elements in a building. These rules were developed over time and are based on the principles of harmony and symmetry. The three main Classical Orders are the Doric Order, the Ionic Order, and the Corinthian Order.
The Doric Order is the simplest and most rustic of the Classical Orders. It is characterized by a plain shaft with no base or capital, and a simple, unadorned cap. The Ionic Order is more elaborate than the Doric Order, with a base and capital that are more ornate. The capital is decorated with a spiral scroll known as a “volute.” The Corinthian Order is the most ornate of the Classical Orders, with a capital that is decorated with leaves and acanthus scrolls.
Classical architecture is known for its use of columns, which are used to support the weight of the building and to create a sense of order and symmetry. Columns are often placed in pairs or in a row, and are decorated with capitals and bases that follow the rules of the Classical Orders. Pediments, which are triangular sections of a building’s roof, are also an important feature of classical architecture. They are often decorated with sculptures or reliefs.
One of the most famous examples of classical architecture is the Parthenon, a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena on the Acropolis in Athens, Greece. The Parthenon was built in the 5th century BCE and is considered one of the greatest examples of classical architecture. It is known for its perfect symmetry and its use of the Doric Order.
Another famous example of classical architecture is the Colosseum in Rome, Italy. The Colosseum was built in the 1st century CE and is considered one of the greatest examples of Roman architecture. It is known for its large size and its use of the Corinthian Order.
In conclusion, classical architecture is a style of building design that originated in ancient Greece and Rome and later evolved during the Renaissance period. It is characterized by its balance, harmony, and symmetry, which is achieved through the use of a set of guidelines and principles known as the “Classical Orders.” Classical architecture is known for its use of columns, pediments, and other decorative elements that follow the rules of the Classical Orders. Examples of famous classical architecture include the Parthenon and the Colosseum.
Examples of Classical Architecture
Classical architecture refers to the style of building design that originated in ancient Greece and Rome and later evolved during the Renaissance period. It is characterized by its use of simple geometric forms, symmetry, and balance. Here are some examples of classical architecture:
- The Parthenon: Located in Athens, Greece, the Parthenon is a famous example of classical architecture. It was built in the 5th century BCE and was originally a temple dedicated to the goddess Athena. The Parthenon is known for its symmetrical design, which includes a central pediment and two side pediments, as well as its use of the Doric order, one of the three main orders of classical architecture.
- The Colosseum: Located in Rome, Italy, the Colosseum is an iconic example of classical architecture. It was built in the 1st century CE and was originally used for gladiatorial contests and other public events. The Colosseum is known for its large, oval shape and its use of the Flavian order, a style of architecture that incorporated elements of both the Doric and Corinthian orders.
- The Pantheon: Also located in Rome, the Pantheon is a famous example of classical architecture. It was built in the 2nd century CE and has been used as a church since the 7th century. The Pantheon is known for its well-preserved interior dome, which is made of concrete and features a circular opening at the top that allows natural light to enter.
- The Temple of Zeus: Located in Olympia, Greece, the Temple of Zeus is a famous example of classical architecture. It was built in the 5th century BCE and was originally a temple dedicated to the god Zeus. The Temple of Zeus is known for its grand scale and its use of the Ionic order, one of the three main orders of classical architecture.
Influence of Classical Architecture on Modern Design
Classical architecture has had a profound influence on modern design, particularly in the realms of urban planning and interior design. Some of the key ways in which classical architecture has influenced modern design include:
- Emphasis on proportion and harmony: Classical architecture placed a strong emphasis on achieving proportion and harmony in design. This principle has been carried forward into modern design, with architects and designers striving to create spaces that are aesthetically pleasing and visually balanced.
- Use of arches and columns: The use of arches and columns was a hallmark of classical architecture, and these elements have been incorporated into modern design in a variety of ways. For example, arches are often used in the design of doorways and entrances, while columns are used to create visual interest and support structural elements.
- Focus on function and purpose: Classical architecture was designed to serve a specific purpose, whether it was to house government offices, temples, or other public buildings. This focus on function and purpose has been carried forward into modern design, with architects and designers striving to create spaces that are functional and serve a specific purpose.
- Use of classical motifs and symbols: Classical architecture was rich in motifs and symbols, many of which have been incorporated into modern design. For example, the use of the classical orders (Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian) is still common in modern architecture, while the use of classical symbols such as the acanthus leaf and the olive branch can be seen in a variety of design contexts.
Overall, the influence of classical architecture on modern design can be seen in a wide range of areas, from the use of classical motifs and symbols to the emphasis on proportion and harmony. By understanding the principles and aesthetics of classical architecture, modern designers are able to create spaces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Gothic Architecture
History and Characteristics of Gothic Architecture
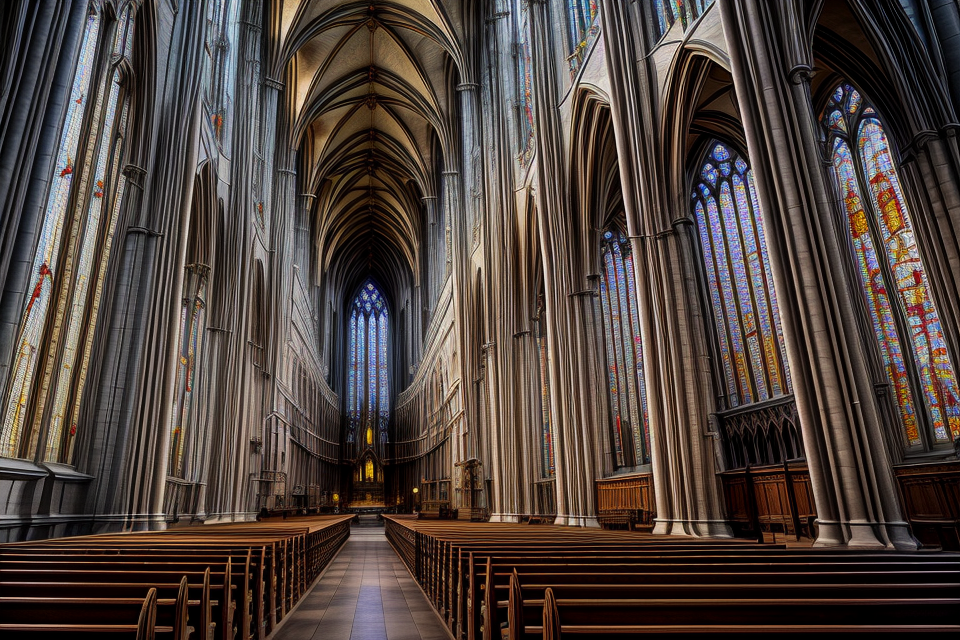
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that emerged in France in the 12th century and flourished throughout Europe until the 16th century. It is characterized by its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, which allowed for the creation of taller and thinner structures with greater windows and more light.
One of the defining features of Gothic architecture is its use of the pointed arch, which allowed for greater verticality and created a sense of upward movement. This was achieved by using a pointed arch with a small radius, which created a thinner and more graceful arch than the round arches used in Romanesque architecture.
Gothic architecture also made use of ribbed vaults, which were made up of intersecting arches that formed a series of pointed curves. These vaults were designed to distribute the weight of the building’s roof more evenly, allowing for thinner walls and larger windows.
Flying buttresses were another key feature of Gothic architecture. These were arches that were supported by exterior pinnacles and served to reinforce the walls of the building, allowing for even greater height and thinner walls.
Gothic architecture was also characterized by its use of light and color. The large windows in Gothic buildings allowed for an abundance of natural light, which was often enhanced by stained glass windows depicting religious scenes and figures.
Overall, Gothic architecture was a revolutionary style that allowed for the creation of soaring, light-filled buildings that were both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Its innovative use of structural elements such as pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses would go on to influence later architectural styles, including Renaissance and Baroque architecture.
Examples of Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that originated in France in the 12th century and later spread throughout Europe. It is characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and large, stained glass windows. Some of the most famous examples of Gothic architecture include:
- Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, France
- Chartres Cathedral in Chartres, France
- Salisbury Cathedral in Salisbury, England
- Cologne Cathedral in Cologne, Germany
- The Hague, city hall in the Hague, Netherlands
- Brussels City Hall in Brussels, Belgium
- Saint Patrick’s Cathedral in Dublin, Ireland
- Rosslyn Chapel in Midlothian, Scotland
- Birmingham Town Hall in Birmingham, England
- Manchester Town Hall in Manchester, England
Each of these buildings has its own unique features and characteristics that make it an excellent example of Gothic architecture. They also have their own stories and history behind them that makes them special and unique. For example, Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris is one of the most famous and recognizable buildings in the world, it was built in the 12th century and it’s a UNESCO World Heritage Site, it’s a symbol of Paris and France, it’s a place of pilgrimage for Catholics and it’s also a great example of Gothic architecture with its famous rose windows, gargoyles and its unique architectural style.
Another example, Rosslyn Chapel in Midlothian, Scotland is a small, intimate chapel built in the 15th century, it’s a great example of Gothic architecture with its intricate stone carvings and unique architectural features. It’s also famous for its association with the Knights Templar and the alleged connection to the Da Vinci Code.
These are just a few examples of the many beautiful and historic buildings that are considered to be excellent examples of Gothic architecture. Each one has its own unique features and characteristics that make it special and worth visiting.
Influence of Gothic Architecture on Modern Design
Gothic architecture, with its intricate details and towering spires, has had a profound influence on modern design. Many of the principles and techniques used in Gothic architecture, such as the use of pointed arches and ribbed vaults, have been adapted and incorporated into modern architectural styles.
One of the most significant ways in which Gothic architecture has influenced modern design is in the use of light and space. Gothic cathedrals were designed to let in as much natural light as possible, creating a sense of grandeur and height. This concept has been carried over into modern design, with architects using large windows and glass facades to bring in natural light and create open, airy spaces.
Another way in which Gothic architecture has influenced modern design is in the use of symmetry and proportion. Gothic buildings were designed to be balanced and harmonious, with each element of the building carefully calculated to create a sense of unity and coherence. This attention to detail and focus on symmetry and proportion can be seen in modern architecture, where architects strive to create buildings that are both aesthetically pleasing and functional.
In addition to these aesthetic influences, Gothic architecture has also had an impact on modern engineering and construction techniques. The use of ribbed vaults and pointed arches in Gothic buildings allowed for thinner walls and greater structural strength, paving the way for the development of new construction methods and materials. These advancements have been crucial in the development of modern engineering and construction practices.
Overall, the influence of Gothic architecture on modern design can be seen in many different aspects of contemporary architecture, from the use of light and space to the attention to detail and focus on symmetry and proportion. Its impact on modern engineering and construction techniques has also been significant, paving the way for new methods and materials that have shaped the built environment as we know it today.
Renaissance Architecture
History and Characteristics of Renaissance Architecture
Renaissance architecture is a style of architecture that emerged in Italy during the 14th century and later spread throughout Europe. The term “Renaissance” means “rebirth,” and this style of architecture marked a significant shift away from the Gothic style that had dominated Europe for centuries.
One of the key characteristics of Renaissance architecture is its emphasis on classical forms and proportions. Architects and artists of the Renaissance looked to the buildings and art of ancient Greece and Rome for inspiration, and sought to imitate the harmony and balance of these classical works.
Another important aspect of Renaissance architecture is its use of linear perspective. Renaissance artists and architects were interested in creating a sense of depth and realism in their work, and used linear perspective to create the illusion of three-dimensional space on a two-dimensional surface.
Renaissance architecture also placed a strong emphasis on mathematics and geometry. Architects used mathematical principles to create buildings with perfectly symmetrical facades and intricate geometric patterns.
In addition to these formal characteristics, Renaissance architecture was also marked by its use of new building materials and techniques. The introduction of steel and brick allowed architects to build taller and more massive structures than had been possible in the past.
Overall, the Renaissance marked a significant shift in architectural style, moving away from the dark and Gothic towards a lighter, more humanistic approach that celebrated the ideals of beauty, harmony, and proportion.
Examples of Renaissance Architecture
The Renaissance period, which spanned from the 14th to the 17th century, is known for its revival of classical styles and the development of new techniques in architecture. Here are some notable examples of Renaissance architecture:
1. Florence Cathedral (Santa Maria del Fiore)
Florence Cathedral, also known as Santa Maria del Fiore, is a prime example of Renaissance architecture. It was designed by Filippo Brunelleschi and built between 1420 and 1436. The cathedral’s dome, which was the largest in the world at the time, was a significant engineering feat and demonstrated the mastery of Renaissance architects over the classical principles of symmetry and proportion.
2. Palazzo della Signoria (Palazzo Vecchio)
The Palazzo della Signoria, also known as the Palazzo Vecchio, is a government palace in Florence, Italy. It was built in the 13th century but underwent significant renovations during the Renaissance period. The palace’s design incorporates both Gothic and Renaissance elements, making it a unique example of the period’s architectural style.
3. St. Peter’s Basilica
St. Peter’s Basilica in Vatican City is one of the most famous examples of Renaissance architecture. It was designed by architects such as Bramante, Raphael, and Michelangelo and took over 100 years to complete. The basilica’s dome, which was designed by Michelangelo, is one of the most iconic features of Renaissance architecture and symbolizes the power and majesty of the Catholic Church.
4. The Medici Villas
The Medici Villas were a series of country estates built for the Medici family outside of Florence during the Renaissance period. The villas were designed by architects such as Giuliano da Sangallo and Bartolomeo Ammannati and were built to showcase the family’s wealth and power. The villas featured lavish gardens, sculptures, and fountains, as well as innovative architectural features such as loggias and arcades.
Overall, these examples demonstrate the diversity and innovation of Renaissance architecture, which blended classical and Gothic styles with new techniques and materials to create some of the most iconic buildings in history.
Influence of Renaissance Architecture on Modern Design
Renaissance architecture, which emerged in Italy during the 14th century, had a profound impact on modern design. This architectural style was characterized by its focus on harmony, proportion, and symmetry, as well as its use of classical motifs and elements from ancient cultures. The influence of Renaissance architecture on modern design can be seen in various aspects, including:
- Emphasis on Functionality and Aesthetics: Renaissance architecture emphasized the importance of both functionality and aesthetics in design. This concept is still relevant in modern design, where architects strive to create structures that are not only visually appealing but also serve their intended purpose effectively.
- Use of Classical Elements: Renaissance architecture incorporated classical elements such as columns, arches, and pediments into its designs. These elements have become timeless and continue to be used in modern architecture to create a sense of grandeur and elegance.
- Revival of Humanism: Renaissance architecture marked the revival of humanism, which emphasized the importance of the human figure in art and design. This philosophy can be seen in modern design, where architects aim to create spaces that are comfortable, functional, and reflective of human needs and desires.
- Importance of Proportion and Symmetry: Renaissance architecture placed a strong emphasis on proportion and symmetry in its designs. This focus on balance and harmony can be seen in modern design, where architects strive to create structures that are visually pleasing and aesthetically balanced.
Overall, the influence of Renaissance architecture on modern design can be seen in the continued use of classical elements, the emphasis on functionality and aesthetics, and the importance of proportion and symmetry. These principles have become timeless and continue to shape the way we design and build our environments today.
Modern Architecture
History and Characteristics of Modern Architecture
Modern architecture emerged in the early 20th century as a response to the industrial revolution and the changing social, economic, and political conditions of the time. It was characterized by a rejection of traditional architectural styles and a focus on functional design and the use of new materials and technologies.
One of the key characteristics of modern architecture is its emphasis on simplicity and functionality. Architects sought to create buildings that were functional and efficient, with clean lines and a lack of ornamentation. This was in contrast to the ornate and decorative styles of traditional architecture.
Another important characteristic of modern architecture is its use of new materials and technologies. Architects experimented with new materials such as steel, concrete, and glass, which allowed for new forms of construction and enabled the creation of taller and more structurally sound buildings.
In addition to its focus on functionality and the use of new materials, modern architecture was also influenced by the principles of the International Style, which emphasized simplicity, functionalism, and the use of industrial materials. The International Style was popularized by architects such as Le Corbusier and Walter Gropius, and had a significant impact on the development of modern architecture.
Overall, modern architecture represents a significant departure from traditional architectural styles, and is characterized by its emphasis on functionality, simplicity, and the use of new materials and technologies.
Examples of Modern Architecture
Modern architecture emerged in the early 20th century and aimed to break away from traditional styles. Some of the most iconic examples of modern architecture include:
- The Guggenheim Museum in New York City, designed by Frank Lloyd Wright in 1959.
- The Seagram Building in New York City, designed by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe in 1958.
- The United Nations Headquarters in New York City, designed by a team led by Wallace Harrison in 1952.
- The Sydney Opera House in Australia, designed by Jørn Utzon in 1973.
- The Le Corbusier’s chapel Notre Dame du Haut in Ronchamp, France in 1955.
These buildings were designed to be functional and efficient, with clean lines and minimal decoration. They often used new materials and construction techniques, such as reinforced concrete and steel frame structures. Modern architecture became a symbol of progress and modernity, and its influence can be seen in many aspects of contemporary design.
Influence of Modern Architecture on Contemporary Design
Modern architecture has had a profound impact on contemporary design, influencing everything from the materials used in construction to the very shapes and forms of buildings. One of the key aspects of modern architecture that has had the most significant impact on contemporary design is its emphasis on functionality and simplicity.
Emphasis on Functionality and Simplicity
Modern architecture sought to move away from the ornate and decorative styles of the past, instead focusing on creating structures that were functional and efficient. This emphasis on functionality has had a lasting impact on contemporary design, with many designers today continuing to prioritize practicality and usability in their work.
Another key aspect of modern architecture that has influenced contemporary design is its use of new materials and technologies. The introduction of materials like steel, glass, and concrete allowed architects to create structures that were lighter, stronger, and more flexible than ever before. This innovation in materials has been carried forward into contemporary design, with designers continuing to explore new technologies and materials to create cutting-edge designs.
Minimalism and Geometric Shapes
One of the most recognizable features of modern architecture is its use of minimalism and geometric shapes. This aesthetic, which was popularized by architects like Le Corbusier and Mies van der Rohe, emphasized simplicity and clarity in design. Today, this minimalist aesthetic can be seen in everything from product design to graphic design, with designers often using simple shapes and clean lines to create bold and striking designs.
Brutalism
Another important aspect of modern architecture that has had an impact on contemporary design is brutalism. Brutalism is a style of architecture that emphasizes raw, exposed concrete as a building material, often using it in bold and dramatic ways. While brutalism was controversial in its time, it has since become a popular style in contemporary design, with many designers embracing its raw, industrial aesthetic.
In conclusion, modern architecture has had a profound impact on contemporary design, influencing everything from the materials used in construction to the very shapes and forms of buildings. Its emphasis on functionality, simplicity, and innovation continues to inspire designers today, with many of its key features and aesthetics becoming central to contemporary design.
Sustainable and Green Architecture
Sustainable and green architecture is a subcategory of modern architecture that focuses on creating buildings that are environmentally friendly and sustainable. This type of architecture takes into account the impact that buildings have on the environment and seeks to minimize that impact by using eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs.
One of the key principles of sustainable and green architecture is the use of renewable energy sources. This can include solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heating and cooling systems. These systems can help to reduce the building’s reliance on non-renewable energy sources and decrease its carbon footprint.
Another important aspect of sustainable and green architecture is the use of energy-efficient materials. This can include insulation, double-paned windows, and energy-efficient lighting. These materials can help to reduce the amount of energy needed to heat and cool the building, which can lead to significant cost savings over time.
In addition to using eco-friendly materials and energy sources, sustainable and green architecture also takes into account the impact that buildings have on the surrounding environment. This can include the use of native plants and trees, permeable pavement, and rainwater harvesting systems. These features can help to reduce the building’s impact on the local ecosystem and promote biodiversity.
Overall, sustainable and green architecture is an important subcategory of modern architecture that seeks to create buildings that are environmentally friendly and sustainable. By using renewable energy sources, energy-efficient materials, and eco-friendly features, these buildings can help to reduce their impact on the environment and promote a more sustainable future.
The Future of Architecture
Modern architecture is constantly evolving, and the future of this architectural style is expected to bring new innovations and technologies. Some of the trends that are shaping the future of modern architecture include:
- Sustainable design: With increasing concern for the environment, architects are exploring new ways to create sustainable buildings that are energy-efficient and have a lower carbon footprint. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, as well as the incorporation of green spaces and water conservation measures.
- Smart technology: The integration of smart technology into buildings is becoming more prevalent, with buildings being designed to adapt to the needs of their occupants. This includes the use of sensors and data analytics to optimize energy usage, as well as the use of artificial intelligence to enhance building security and safety.
- Biophilic design: As people spend more time indoors, there is a growing interest in creating buildings that promote a connection with nature. Biophilic design incorporates natural elements, such as plants and natural light, into buildings to improve the well-being of occupants.
- Mixed-use developments: The trend towards mixed-use developments, which combine residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, is expected to continue. This approach to urban planning aims to create more livable and sustainable cities by reducing the need for car travel and promoting walkability.
Overall, the future of modern architecture is expected to be characterized by a focus on sustainability, innovation, and the creation of buildings that meet the changing needs of society.
Recap of the Four Main Types of Architecture
In architecture, there are four main types: modern, traditional, postmodern, and regional. Each type has its unique characteristics and features that set it apart from the others.
- Traditional Architecture: This type of architecture is characterized by its adherence to traditional building methods and styles. It often incorporates classical elements such as columns, pediments, and cornices. Traditional architecture is commonly found in historic buildings and can be seen in various styles, including Gothic, Renaissance, and Baroque.
- Postmodern Architecture: Postmodern architecture is a reaction to modernism and is characterized by its use of historical references and eclectic styles. It often incorporates elements from different time periods and styles, resulting in a fragmented and ironic approach to architecture. Postmodern architecture can be seen in buildings such as the Walt Disney Concert Hall in Los Angeles and the Palacio de Congresos in A Coruña, Spain.
- Regional Architecture: Regional architecture is characterized by its use of local materials and building techniques. It often reflects the cultural and environmental characteristics of a particular region. Examples of regional architecture include Tudor architecture in England, Spanish Colonial architecture in the Americas, and Indo-Saracenic architecture in India.
- Modern Architecture: Modern architecture is characterized by its simplicity, functionality, and use of industrial materials such as steel and glass. It emerged in the early 20th century as a reaction to the ornate and decorative styles of traditional architecture. Modern architecture is often associated with the International Style, which emphasizes function over form and is characterized by its use of flat roofs, horizontal lines, and a lack of decoration. Examples of modern architecture include the Seagram Building in New York City and the Barbican Centre in London.
The Importance of Understanding Architectural Styles
Understanding the various architectural styles is crucial for architects, designers, and individuals who appreciate the built environment. This knowledge allows them to identify and analyze different design elements, which in turn helps them understand the history, culture, and context of a building or structure. By studying the characteristics and features of each style, professionals can gain insight into the principles and techniques used by architects and designers, which can be applied to contemporary designs. Furthermore, understanding architectural styles helps in preserving and protecting our architectural heritage, as it allows us to appreciate and maintain the historical and cultural significance of these structures.
The Impact of Architecture on Society and Culture
Architecture has a profound impact on society and culture, and this is particularly true of modern architecture. This style of architecture emerged in the early 20th century and is characterized by its use of industrial materials, such as steel and glass, and its emphasis on functional design.
One of the key ways in which modern architecture has impacted society and culture is through its influence on urban planning. Modern architects sought to create functional, efficient cities that could accommodate the needs of a rapidly growing population. This led to the development of new technologies and building materials, as well as innovative approaches to urban design.
Modern architecture has also had a significant impact on the way we live and work. By emphasizing functional design, modern architects were able to create buildings that were more efficient and easier to maintain. This has led to the widespread adoption of modern architectural principles in commercial and residential buildings alike.
Another way in which modern architecture has impacted society and culture is through its influence on art and design. The clean lines and minimalist aesthetic of modern architecture have inspired generations of artists and designers, and have helped to shape the look and feel of modern art and design.
Overall, the impact of modern architecture on society and culture has been profound and far-reaching. By emphasizing functional design and the use of industrial materials, modern architects have helped to shape the way we live, work, and interact with our built environment.
FAQs
1. What are the four main types of architecture?
The four main types of architecture are Classical, Gothic, Renaissance, and Modern.
2. What is Classical architecture?
Classical architecture is a style of architecture that originated in ancient Greece and Rome. It is characterized by its use of columns, pediments, and other elements that are derived from ancient Greek and Roman architecture.
3. What is Gothic architecture?
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that emerged in Europe during the Middle Ages. It is characterized by its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses.
4. What is Renaissance architecture?
Renaissance architecture is a style of architecture that emerged in Italy during the 14th century. It is characterized by its use of classical forms and motifs, as well as its emphasis on symmetry and harmony.
5. What is Modern architecture?
Modern architecture is a style of architecture that emerged in the early 20th century. It is characterized by its use of industrial materials and techniques, as well as its emphasis on function and simplicity.